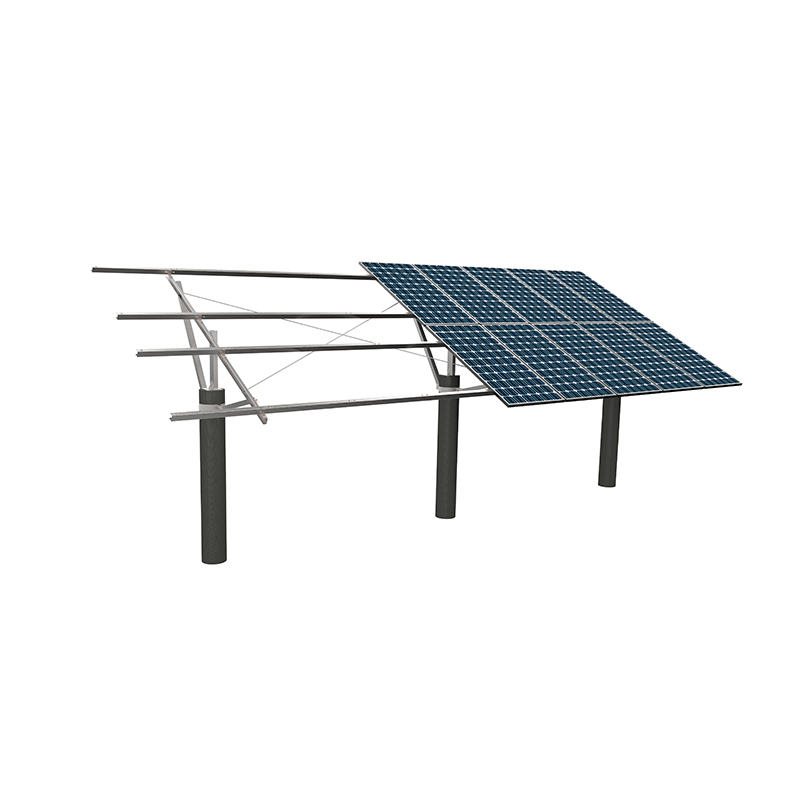
What environmental factors should be considered when installing a ground PV mounting system?
Wind speed and wind load
Wind speed is one of the main environmental factors affecting the structural design and installation of ground photovoltaic mounting systems. There are large differences in wind speed in different regions, and the wind speed varies significantly with time and seasons. The mounting system must have sufficient wind resistance to prevent the structure from deforming, loosening or even collapsing due to wind force. The wind load standard is usually determined based on the local extreme wind speed data and combined with relevant national or local specifications during design. During the installation process, the foundation and the support should be firmly connected to reduce the impact of wind vibration on the stability of the system. At the same time, changes in wind direction will also affect the stress state of the support. Therefore, a detailed wind load simulation analysis should be carried out during the design phase to ensure that it can be safely loaded in all directions.
Terrain undulation and geomorphic conditions
The terrain has a significant impact on the layout and foundation design of the ground photovoltaic mounting system. Flat terrain is easier to construct, and the support installation is relatively simple and the structure is unified; while slopes or hilly areas need to consider the foundation differences and drainage problems caused by the terrain undulation. In areas with large slopes, a graded step foundation or a special support adjustment structure may be required to maintain the optimal inclination and power generation efficiency of the photovoltaic modules. When the terrain is complex, on-site measurement and terrain modeling become important parts of the design. During installation, foundation scouring and flooding caused by concentrated terrain water flow should also be avoided to ensure the long-term stability of the structure.

Soil type and bearing capacity
The type and physical properties of the soil directly determine the selection and construction method of the foundation structure. There are significant differences in the bearing capacity of different soils such as sand, clay, gravel, and silt for pile foundations or concrete foundations. In soft soil, the foundation is prone to settlement or tilt, and reinforcement measures or deeper pile foundations need to be taken. Hard rock or dense soil is conducive to foundation stability, but the construction is more difficult. The assessment of soil moisture content and drainage conditions is also very important. Long-term humid soil environment may cause foundation corrosion or expansion. During installation, the foundation form and size must be reasonably selected according to the soil survey report to ensure the safe operation of the bracket system.
Precipitation and drainage conditions
Precipitation is another key environmental factor affecting the service life and operation safety of ground photovoltaic bracket systems. In areas with high precipitation, especially those with frequent rainy seasons or heavy rains, special attention should be paid to the scouring and water accumulation of the foundation by water flow. Water accumulation not only affects the bearing capacity of the soil, but may also cause moisture in electrical equipment, increasing the difficulty of maintenance. During installation, the bracket layout should be reasonably designed to ensure the smooth discharge of surface water, and combined with facilities such as drainage ditches or drainage pipes to reduce the erosion of the bracket foundation by water accumulation. The drainage design should also take into account extreme weather conditions to avoid local water accumulation or flooding caused by sudden heavy rains.
Temperature changes and thermal expansion and contraction effects
The day and night fluctuations and seasonal changes in temperature will cause thermal expansion and contraction of the bracket material, generating stress on the connectors and the overall structure. The difference in thermal expansion coefficients of different materials will also affect the long-term stability of the structure. Especially in areas with large temperature differences, such as plateaus and the north, the thermal expansion and contraction properties of the material must be fully considered during design, and a reasonable connection method should be adopted to alleviate stress concentration. During installation, the gap design between components and the preload control of fasteners should also adapt to the influence of temperature changes to avoid structural damage or loosening due to stress accumulation.
Earthquake intensity and earthquake-resistant design
In earthquake-prone areas, the installation of ground photovoltaic bracket systems must comply with relevant earthquake-resistant design specifications. Under the action of earthquakes, the structure not only needs to withstand inertial forces, but may also be affected by horizontal and vertical movements of the ground. When designing, it is usually necessary to divide the local earthquake intensity and conduct earthquake load analysis to ensure that the foundation and bracket structure have sufficient earthquake resistance. During the installation process, attention should be paid to the reinforcement of the foundation and the tightening of the connectors to prevent loosening and displacement caused by vibration. In addition, the earthquake-resistant design should also take into account the overall stiffness and toughness of the system to reduce the impact of earthquakes on operational safety.
Other environmental factors
In addition to the above-mentioned main environmental factors, the installation of photovoltaic brackets also needs to consider special environmental conditions such as wind and sand, salt spray, and ultraviolet radiation. In deserts or arid areas, wind and sand may cause wear and tear on the bracket surface and photovoltaic modules, affecting their service life; salt spray corrosion in coastal areas places higher requirements on the anti-corrosion performance of materials. The long-term effect of ultraviolet radiation may also cause coating aging and material performance degradation. In view of these factors, the rational application of material selection and surface treatment technology, as well as the formulation of regular maintenance plans, are important measures to ensure the reliable operation of the bracket system.
Summary table of environmental factors
Environmental Factors Affecting Ground-Mounted Photovoltaic mounting systems
|
Environmental Factor |
Impact Description |
Installation Countermeasures |
|
Wind Speed and Wind Load |
Affects structural stability and safety |
Design according to wind load standards; reinforce foundation |
|
Terrain Variation |
Influences layout and foundation type |
Use stepped foundations; precise site surveying and layout |
|
Soil Type |
Determines foundation bearing capacity and construction difficulty |
Select suitable foundation scheme based on soil investigation |
|
Precipitation and Drainage |
Affects foundation stability and electrical equipment safety |
Design proper drainage to avoid water accumulation and erosion |
|
Temperature Variation |
Causes thermal expansion and contraction affecting structural connections |
Design gaps and connection methods to accommodate thermal changes |
|
Seismic Intensity |
Influences seismic design requirements |
Follow seismic codes; reinforce foundation |
|
Sand and Salt Spray |
Causes material corrosion and wear |
Use corrosion-resistant materials and perform regular maintenance |
|
Ultraviolet Radiation |
Leads to surface coating aging and performance degradation |
Use UV-resistant coatings |



 English
English 日本語
日本語 Deutsch
Deutsch عربى
عربى 中文
中文



