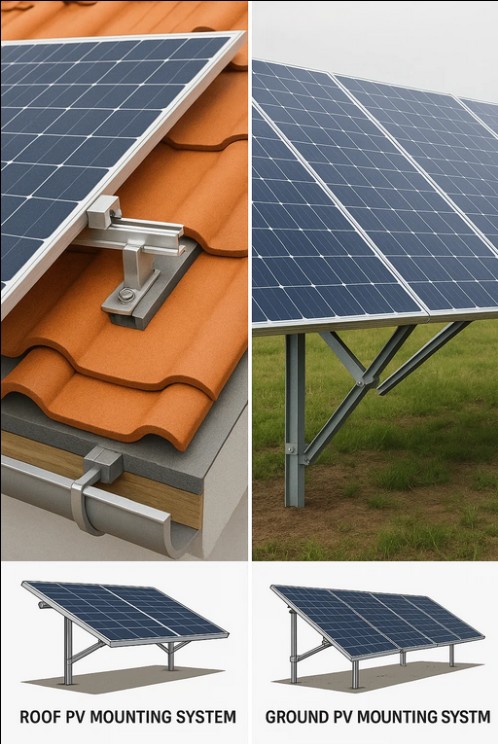
Comparison of Roof PV Mounting System vs. Ground PV Mounting System
Introduction
With the continuous growth of renewable energy demand, photovoltaic (PV) power generation systems have become one of the key technologies for sustainable development. Among the various PV system installation types, roof PV mounting systems and ground PV mounting systems are two of the most commonly adopted methods. Both approaches have their own characteristics, advantages, and limitations. The comparison between these two installation systems provides valuable insights for enterprises, households, and project developers when making investment and design decisions. By examining their structural design, land use efficiency, cost, maintenance requirements, and adaptability, it becomes possible to select the most appropriate system for different application scenarios.
Structural Design and Installation Characteristics
Roof PV mounting systems are directly installed on the roofs of residential, commercial, or industrial buildings. They make use of existing building structures to support solar panels. The installation can vary depending on roof type, such as flat roofs or sloped roofs, and often requires customized mounting brackets to ensure safe integration with the building. In contrast, ground PV mounting systems are installed on open land. Their supporting structures are generally adjustable, which allows developers to optimize panel orientation and tilt angle for maximum solar energy capture. Compared with rooftop installations, ground-mounted systems usually have fewer restrictions in terms of space and design flexibility, but they require land availability as a prerequisite.
| Factor | Roof PV Mounting System | Ground PV Mounting System |
|---|---|---|
| Installation Base | Existing building roof | Independent land foundation |
| Tilt Angle | Limited by roof | Flexible, adjustable |
| Space Requirement | No additional land | Dedicated land required |
| Integration | Requires building compatibility | Independent design |

Land Utilization and Space Efficiency
One of the main differences between roof-mounted and ground-mounted systems is land utilization. Roof PV systems utilize the roof area of buildings, which means no additional land is occupied. This makes them suitable for urban or densely populated regions where land is scarce. Ground PV systems, on the other hand, occupy dedicated plots of land. While this might raise concerns about land competition with agriculture or other industries, it allows for larger-scale installations that may not be feasible on roofs. For projects that require high energy output, ground systems are often the more practical option, but for households and small businesses, roof systems provide an efficient use of otherwise unused space.
|
Category |
Roof PV Mounting System |
Ground PV Mounting System |
|
Land usage |
No additional land required |
Requires dedicated land area |
|
Space limitation |
Restricted by roof size |
Large-scale installations possible |
|
Typical application scale |
Small to medium projects |
Medium to large projects |
Installation Cost and Investment Considerations
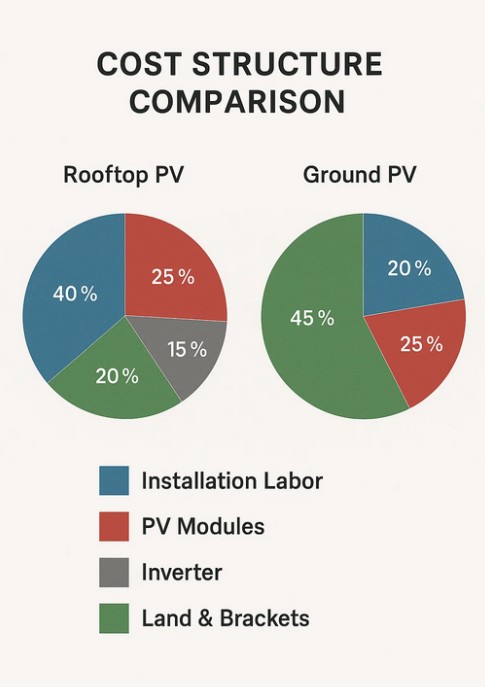
Cost is an important factor when comparing these two systems. Roof PV systems generally have lower costs for land use since they utilize existing building structures. However, installation complexity can increase expenses if roofs have irregular shapes or require reinforcement. Ground PV systems usually have higher initial costs due to land preparation, foundation construction, and supporting structures. Nevertheless, ground systems often allow for economies of scale, making them cost-efficient for large projects. The overall investment decision depends on available land resources, expected energy output, and long-term return on investment.
Energy Efficiency and Performance
Energy performance varies between roof and ground PV systems. Roof systems are subject to limitations such as roof orientation, tilt angle, and potential shading from nearby buildings or trees. This can reduce energy output compared to ground systems. Ground-mounted systems provide greater flexibility in aligning panels to the optimal angle and direction, which enhances solar capture efficiency. Moreover, ground systems often benefit from better airflow around panels, helping with cooling and improving energy yield. While rooftop systems can still achieve satisfactory efficiency, their performance is more dependent on site-specific roof conditions.
| Performance Factor | Roof PV Mounting System | Ground PV Mounting System |
|---|---|---|
| Orientation | Restricted | Adjustable (tracking optional) |
| Shading Risk | Higher in urban | Lower in open fields |
| Cooling Effect | Moderate | Better airflow |
| Output Potential | Dependent on roof | Optimized |
Maintenance and Accessibility
Maintenance is another area where differences are evident. Roof PV systems are less accessible due to their elevated installation position. Cleaning panels, inspecting wiring, and repairing equipment on roofs can be more time-consuming and may involve safety risks. Ground PV systems, on the other hand, are easier to access for routine maintenance and repairs. Technicians can carry out inspections without special safety equipment, reducing service costs over time. However, roof systems have the advantage of being less prone to dust accumulation compared to ground systems in some regions, especially where soil or sand may increase soiling rates.
Durability and Reliability
Both roof and ground PV systems are designed to withstand environmental stresses such as wind, rain, and temperature changes. Roof systems rely heavily on the structural integrity of the building, which means additional considerations must be taken to ensure the roof can bear the load. Ground systems are typically built with more robust foundations, allowing them to endure stronger environmental forces. Nevertheless, ground-mounted systems might be more exposed to risks such as flooding, while roof systems can sometimes offer more protection from ground-level hazards.
Environmental Impact and Aesthetic Factors
Roof-mounted PV systems have minimal impact on the surrounding environment since they use pre-existing structures. Their installation often improves building sustainability without altering land use patterns. Ground-mounted systems, however, can affect landscapes and ecosystems, especially when installed on agricultural or forest land. Careful planning is required to minimize ecological impact. From an aesthetic perspective, roof systems are generally less intrusive as they blend into the building, while large-scale ground systems can significantly change the visual landscape of an area.
| Aspect | Roof PV System | Ground PV System |
|---|---|---|
| Land Use | Efficient | Land intensive |
| Ecosystem Impact | Minimal | Possible habitat disruption |
| Visual Impact | Low | Higher |
Application Scenarios
Roof PV mounting systems are most suitable for residential, commercial, and small industrial applications where roof space is sufficient to meet energy needs. They are widely adopted in urban areas and regions with limited land availability. Ground PV systems are best for utility-scale solar farms and industrial applications that require high energy output. They are particularly advantageous in rural or suburban areas where large tracts of land can be dedicated to solar energy production. The choice between the two depends largely on project goals, available resources, and local regulations.
|
Application Type |
Recommended System |
|
Residential households |
Roof PV Mounting System |
|
Urban commercial buildings |
Roof PV Mounting System |
|
Utility-scale solar farms |
Ground PV Mounting System |
|
Industrial energy demand |
Ground PV Mounting System |



 English
English 日本語
日本語 Deutsch
Deutsch عربى
عربى 中文
中文



